This is the 4th blog of our series on NAAC accreditation.
After looking at NAAC’s assessment criteria, SSR, and accreditation policies, we can now see what the grading system is, and how the grades are measured.
But before we get into all that, there is something else you should know:
The period of validity of the accreditation: The accreditation status is valid for five years from the date of approval by the Executive Committee of the NAAC.
Now back to the topic at hand.
There are two types of outcomes for assessment and accreditation
1. Peer Team Report
The qualitative part of the outcome is called Peer Team Report (PTR) which is an objective report prepared by the team visiting the institution.
2. Institutional Grading
The quantitative part of the outcome comprises the criterion-wise quality assessment, with the final Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA), a letter grade and a performance descriptor. The CGPA and letter grade are the certification by the NAAC on institutional accreditation. Thus, at the end of A&A process, the institution will be awarded with a letter grade to represent its quality level along with its performance descriptor and accreditation status. This will be based on the CGPA earned by it through the assessment process, as mentioned in the image below:
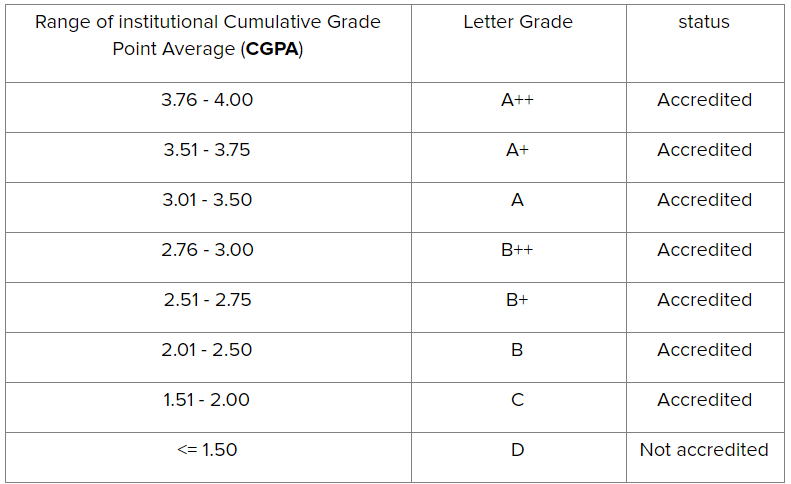
Institutions which secure a CGPA less than or equal to 1.50 will be classified by the NAAC as “assessed and found not qualified for accreditation”.
The seven criteria is further divided into “Key Aspects”. Certain important assessment Indicators are identified under the key aspects and the seven criteria which leads the peer team members to measure the various quality parameters. These indicators help the calculation of the Key Aspect-wise Grade Points (KA-GPS) and the Criterion-wise Grade Point Averages (CR-GPAs) in order to conclude the quality status of the institution.
The assessment indicator guidelines are used for arriving at the Key Aspect Grade Points (KAGP). The Key Aspects (sub criterions) under each criterion have their own weightages based on their importance while computing the CGPA. Thus, the grade points assigned to different Key Aspects (sub criterions) and Criteria gets normalized at two levels, before the final CGPA is calculated.
Key Aspect-wise Weighted Grade Point (KAWGP)
NAAC has assigned predetermined weightages to each of the key aspects under the seven criteria. To help the peer team to arrive at KAGP, NAAC provides certain guiding indicators. The peer team is expected to assign appropriate grade point to each of the key aspect by using five point scale (0–4). They can do this by using the guiding indicators and based on their observations and assessment of the institution (onsite visit and the validation of SSR). These grade points are assigned as 0/1/2/3/4 without using decimal points and are referred to as the Key Aspect-wise Grade Points (KAGP).
Unlike in the earlier methodology where the letter grades were converted to grade points, the current methodology directly assigns the grade points without assigning any letter grades.
The Key Aspect-wise Weighted Grade Point (KAWGP) is calculated by multiplying the predetermined Weightage (W) of a Key Aspect with respective KAGP assigned by the peer team. i.e.,
KAWGPi=KAGPi * Wi
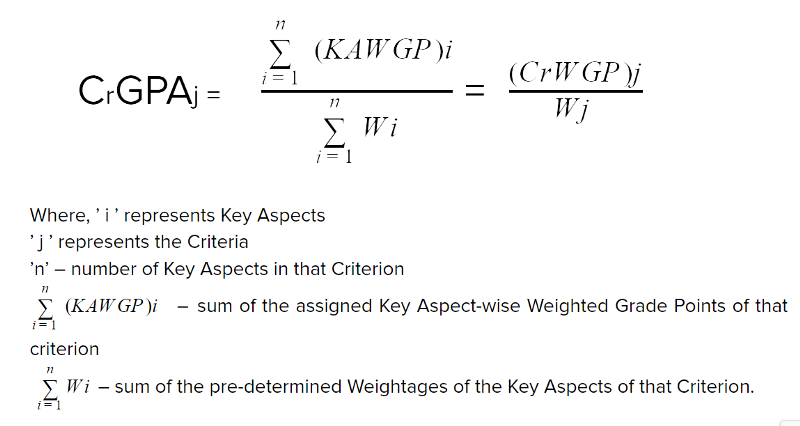
Calculation of CrGPA
Criterion-wise Grade Point Average CrGPA is calculated by dividing the sum of the Key Aspect-wise Weighted Grade Points (KAWGP) of a Criterion by sum of the weightages of the Key Aspects of that Criterion. This also can be calculated by dividing the Criterion-wise Weighted Grade Point (CrWGP) by the total weightage of that criterion as given below.
Calculation of CGPA
The sum of the seven CrWGP divided by the sum of the pre assigned weightages of the seven criteria will result in Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) of the institution. The institutional CGPA will be the deciding factor for accreditation status of the institution and its grade.
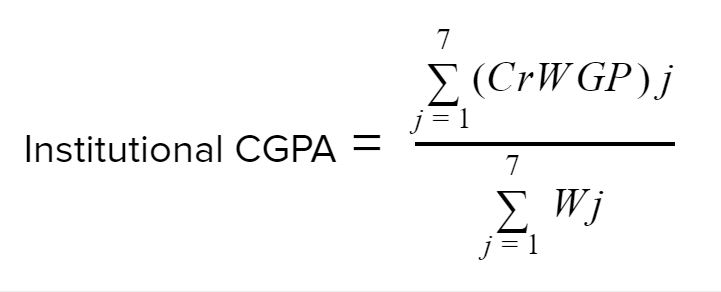
So that is how the NAAC calculates the final CGPA and arrive at the decision of whether or not to give accreditation for the institution.
In the coming blogs of this series, we will discuss other decisive steps during the accreditation like the Internal Quality Assurance Cell (IQAC) and the Letter of Intend (LOI).




